The Simple Truth of Vitamin B-Complex

You may have noticed that B-complex supplements have rapidly gained popularity over the last several years for their claims to revamp energy levels. The B vitamins indeed have a part to play in energy levels but their true role in the overall function of the body remains widely misunderstood.
Breaking Down The Bs
When a vitamin formulation contains all eight B vitamins (along with potentially up to one or two other ingredients) it’s marketed as a B-complex supplement rather than a multivitamin. Vitamin B1, 2, 3, 5 6, 7, 9, and 12 comprise all B-complex products. There are many variations of B-complex supplements on the market because each brand individually decides on the level of each B vitamin to include in their product. Let’s take a closer look at each of the eight B vitamins in these products to better understand what role each play.
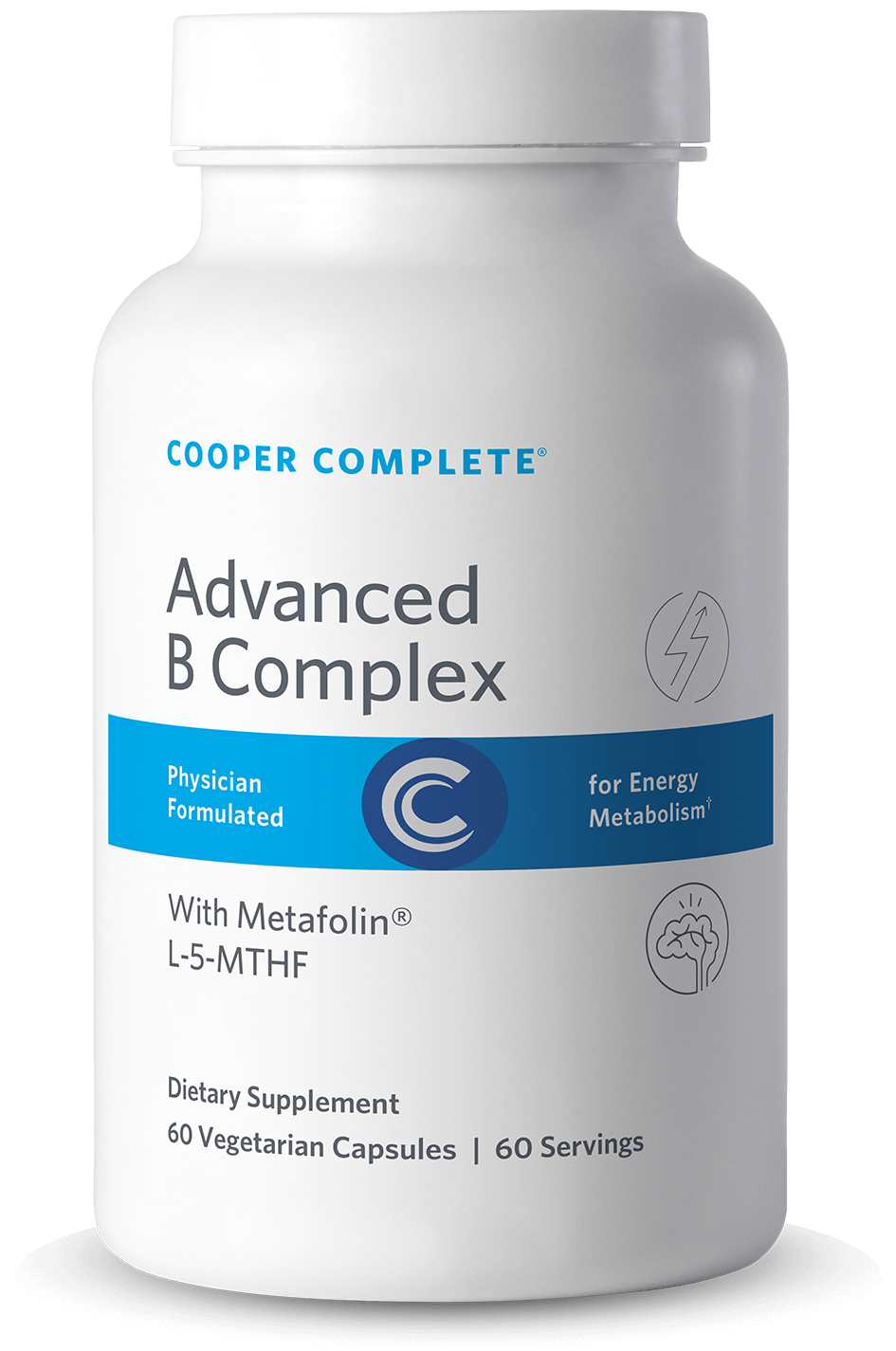
Advanced B Complex Supplement
Advanced Vitamin B Complex supplement contains the activated, methylated, most easily absorbable forms of eight essential B vitamins, including biotin and folate, to support energy production and immune, cardiovascular, and neurological health.†
$23.68 Add to cart- Vitamin B1 (thiamine): This essential nutrient enables the proper function of all the body’s tissues and helps the body convert food into energy. Thiamine is most commonly found in food sources such as pork, chicken, legumes, rice, fortified bread, and pasta.
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin): Riboflavin is involved in metabolic processes within the body and is necessary for proper cell function and energy production. This B vitamin can be found in milk, meat, eggs, nuts, enriched flour, and green vegetables. It is used for treating acne and muscle cramps as well as the prevention of migraine headaches.
- Vitamin B3 (niacin): Niacin acts as an antioxidant and plays a key role in cell signaling, DNA repair, lowering cholesterol, and managing arthritis symptoms.
- Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid): This particular B vitamin is necessary for blood cell production, supporting a healthy digestive tract and contributing to the proper function of the nervous system. It is also responsible for producing sex and stress-related hormones as well as promoting healthy skin, hair, and eyes.
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine): Vitamin B6 is crucial for normal brain development and metabolism. While its main role lies in creating neurotransmitters and regulating homocysteine levels, it is also important in supporting a healthy immune system.
- Vitamin B7 (biotin): Biotin is most well-known for its link to hair, skin, and nail health. The majority of biotin consumption in a healthy diet comes from meat. This B vitamin helps form the building blocks of enzymes to break down food but its absorption can be inhibited by chronic alcoholic consumption.
- Vitamin B9 (folate or folic acid): Folate (also known as folic acid) is a key player in cell growth and DNA formation. Leafy greens are said to be the main dietary source of vitamin B9.
- Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin and methylcobalamin): Vitamin B12 aids in cell metabolism, nerve function, and DNA production. Contrary to popular opinion, taking B12 which exceeds normal amounts does not increase energy levels. In fact, the NIH states specifically that “except in people with a vitamin B12 deficiency, no evidence shows that vitamin B12 supplements increase energy or improve athletic performance.” This misconception of energy production stems from its role in helping every cell’s metabolism in the body. And while a deficiency of B12 can lead to tiredness or weakness, returning to healthy levels of B12 restores normal energy levels but there is no evidence of boosting energy. Vitamin B12 can only be found in animal protein, fish, and dairy.
Too Much Of A Good Thing
B vitamins primarily play an important role in cellular metabolism as well as maintaining optimal brain function and heart health. Certain brands advertise that their product maximizes the health benefits by combining all eight of the B vitamins into one B-complex supplement. However, when it comes to vitamin B, taking higher doses doesn’t actually contribute to higher vitamin levels or better health.
Cooper Complete aims to design products to help people improve the quality and quantity of life by working directly with Cooper Clinic and reviewing the science. It has been shown that B vitamins are water-soluble, which means that our bodies naturally eliminate any excess amounts of B vitamins ingested through the digestive system. Most generally healthy people do not have vitamin B deficiencies so introducing mega doses of these particular vitamins is unnecessary. The majority of B vitamins, with the exception of vitamin B12, are found in food sources such as:
- Dark, leafy vegetables including spinach and kale
- Citrus fruits and bananas
- Avocados
- Almonds, sunflower seeds
- Eggs and dairy products
- Legumes
- Whole grains
Health Concerns Surrounding Mega Doses Of Vitamin B
Consuming mega doses of other B-complex products can lead to serious health concerns. For example:
- Vitamin B1: When the amount of vitamin B1, also known as thiamine, exceeds normal levels in the body it can cause hypertension or high blood pressure.
- Vitamin B6: High doses of vitamin B6, or pyridoxine, can cause nerve damage or skin lesions.
- Vitamin B9: High amounts of vitamin B9, more popularly known as folic acid or folate, can often mask vitamin B12 deficiency.
Cooper Complete Multivitamins Compared to B-Complex Supplements
See the chart below for a side-by-side comparison of popular vitamin B-complex supplements on the market and their vitamin B levels.
B Complex Vitamin Comparisons to Multivitamins |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily Value | Original♥ Multivitamin | Basic One♥ Multivitamin | Advanced B Complex | Solgar B-Complex 100♣ | |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) | 1.2 mg | 3 mg | 1.5 mg | 100 mg | 100 mg |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | 1.3 mg | 10 mg | 2 mg | 12.7 mg | 100 mg |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) | 16 mg | 20 mg | 20 mg | 108 mg | 100 mg |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | 5 mg | 10 mg | 10 mg | 100 mg | 100 mg |
| Vitamin B6 (as Pyridoxine HCI) | 1.7 mg | 10 mg | 10 mg | 16.7 mg | 100 mg |
| Vitamin B7 (Biotin) | 30 mcg | 300 mcg | N/A | 400 mcg | 100 mcg |
| Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid) | 400 mcg DFE | Metafolin® Folate 333 mcg DFE (200 mcg L-5-MTHF) | Metafolin® Folate 333 mcg DFE (200 mcg L-5-MTHF) | Metafolin® Folate 667 mcg DFE (400 mcg L-5-MTHF) | Folate 666 mcg DFE (400 mcg folic acid) |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.4 mcg Methylcobalamin | 400 mcg Methylcobalamin | 400 mcg Methylcobalamin | 400 mcg Methylcobalamin | 100 mcg Cyanocobalamin |
♥Partial Ingredient List
♣Also contains Choline and Inositol.
Let science speak for itself. If you find yourself spending money on B-complexes in an attempt to increase your energy levels, remember that your body will not be fooled−it will only absorb as much as it needs. It is not safe to assume that it is effective to take high doses of any vitamin making it important to be aware of the appropriate amount of vitamin B your body needs and supplement your diet accordingly.
As a reminder, your physician understands your health profile best, so it’s important to talk to him or her about which supplements are best for you.